MatheAss 10.0 - Linear Algebra
Systems of linear equations
The program determines the solution vector from a system of linear equations with n equations and n unknowns.
Example: Looking for a parabola through the points P (1|3), Q (2|1) and R (4|9) leads to the system of equations
1·x1 + 1·x2 + 1·x3 = 3
4·x1 + 2·x2 + 1·x3 = 1
16·x1 + 4·x2 + 1·x3 = 9
L = (2; -8; 9)
So the parabola has the equation y = 2x 2 - 8x + 9.
Example with two-dimensional Solution space:
0·x1 + 0·x2 + 2·x3 - 1·x4 = 1
1·x1 + 1·x2 + 1·x3 + 1·x4 = 4
2·x1 + 2·x2 - 4·x3 + 5·x4 = 5
1·x1 + 1·x2 - 7·x3 + 5·x4 = 0
L = { ( 3,5-s-1,5t; s; 0,5+0,5t; t ) | s,t ∈ R }
 Linear Optimization
(since February 2022)
Linear Optimization
(since February 2022)
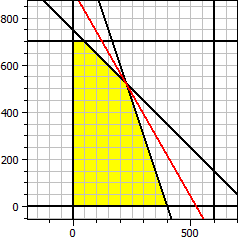
The program determines the optimal solution for a two-variable objective function with linear inequalities as constraints.
Objective function: ƒ(x,y) = 140·x + 80·y → Maximum Constraints: x ≥ 0 y ≥ 0 x ≤ 600 y ≤ 700 x + y ≤ 750 3·x + y ≤ 1200 Maximum: x = 225 y = 525 ƒ(x,y) = 73500
 Linear combination
Linear combination
The program determines the linear combination of a vector from three given vectors. The routine is also suitable for checking the linear independence of three vectors in space, i.e. whether they lie in one plane.
⎧ 1 ⎫ ⎧ 1 ⎫ ⎧ 1 ⎫ ⎧ 2 ⎫
a·⎪ 0 ⎪ + b·⎪ 1 ⎪ + c·⎪ 1 ⎪ = ⎪ 3 ⎪
⎩ 0 ⎭ ⎩ 0 ⎭ ⎩ 1 ⎭ ⎩ 4 ⎭
Solution:
a = -1 b = -1 c = 4
 Scalar product
Scalar product
The program calculates the scalar product of two vectors, the length of the two vectors and the included angle.
-> ⎧ 1 ⎫ -> ⎧ 5 ⎫
a = ⎪ 3 ⎪ b = ⎪ 0 ⎪
⎩ 1 ⎭ ⎩ 3 ⎭
Scalar product of the vec. = 8
Length of the first vector = √11 = 3.32
Length of the second vector = √34 = 5.83
included angle α = 65.56°
 Vector product
Vector product
The program calculates the vector product and its amount for two vectors. The vector product is perpendicular to the parallelogram spanned by you, and its amount is equal to the area of the parallelogram.
-> ⎧ 1 ⎫ -> ⎧ 7 ⎫
a = ⎪ 2 ⎪ b = ⎪ 1 ⎪
⎩ 3 ⎭ ⎩ 4 ⎭
-> -> ⎧ 5 ⎫ -> ->
a x b = ⎪ 17 ⎪ |a x b|= √483 = 21,977261
⎩-13 ⎭
 Triple Product
Triple Product
The program calculates the late product for three vectors. Its amount indicates the volume of the displaced cuboid (spatula) that is spanned by the three vectors.
-> ⎧ 2 ⎫ -> ⎧ 2 ⎫ -> ⎧ 3 ⎫
a = ⎪ 3 ⎪ b = ⎪-1 ⎪ c = ⎪ 9 ⎪
⎩ 5 ⎭ ⎩ 7 ⎭ ⎩ 2 ⎭
-> -> ->
( a x b ) · c = 26
 Matrix Inversion
Matrix Inversion
The program calculates the determinant, the rank and the inverse matrix for a square matrix of order n.
Matrix : ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ ⎧ 1 0 2 ⎫ ⎪ 0 1 0 ⎪ ⎩ 3 0 1 ⎭ Inverse Matrix : ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ ⎧-0,2 0 0,4 ⎫ ⎪ 0 1 0 ⎪ ⎩ 0,6 0 -0,2 ⎭ Order = 3, Rank = 3, Determinant = -5
 Pseudoinverse Matrix
Pseudoinverse Matrix
If the columns of a matrix A are linearly independent, then
A+ = ( AT· A )-1· AT
It is A + is a left inverse of A , that is, it applies:
Matrix A ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ ⎧ 1 1 1 1 ⎫ ⎩ 5 7 7 9 ⎭ AT· A ¯¯¯¯¯ ⎧ 26 36 36 46 ⎫ ⎪ 36 50 50 64 ⎪ ⎪ 36 50 50 64 ⎪ ⎩ 46 64 64 82 ⎭ AT· A is not invertible A · AT ¯¯¯¯¯¯ ⎧ 4 28 ⎫ ⎩ 28 204 ⎭ ( A · AT )-1 ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ ⎧ 6,375 -0,875 ⎫ ⎩-0,875 0,125 ⎭ Right Inverse: AT·( A·AT )-1 ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ ⎧ 2 -0,25 ⎫ ⎪ 0,25 0 ⎪ ⎪ 0,25 0 ⎪ ⎩ -1,5 0,25 ⎭
 Matrix Multiplication
Matrix Multiplication
The program calculates the product matrix for two matrices.
1. Matrix : ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ ⎧ 1 0 2 ⎫ ⎩ 0 1 0 ⎭ 2. Matrix : ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ ⎧-0,2 0 0,4 1 ⎫ ⎪ 0 1 0 1 ⎪ ⎩ 0,6 0 -0,2 1 ⎭ Product Matrix: ¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯ ⎧ 1 0 0 3 ⎫ ⎩ 0 1 0 1 ⎭